[ad_1]

Win McNamee
The Thesis
At the end of 2021, the Invesco QQQ ETF (NASDAQ:QQQ), which tracks the Nasdaq 100, reached a PE of 39 and a cyclically adjusted PE (CAPE ratio) of 60. Legendary investor George Soros has believed for many years that excess on the upside leads to excess on the downside. QQQ could fall much, much further as the excess drains out of its valuation. History has shown that when the CAPE ratio reaches 60, real returns for the following 15 years settle around negative 4% per annum:
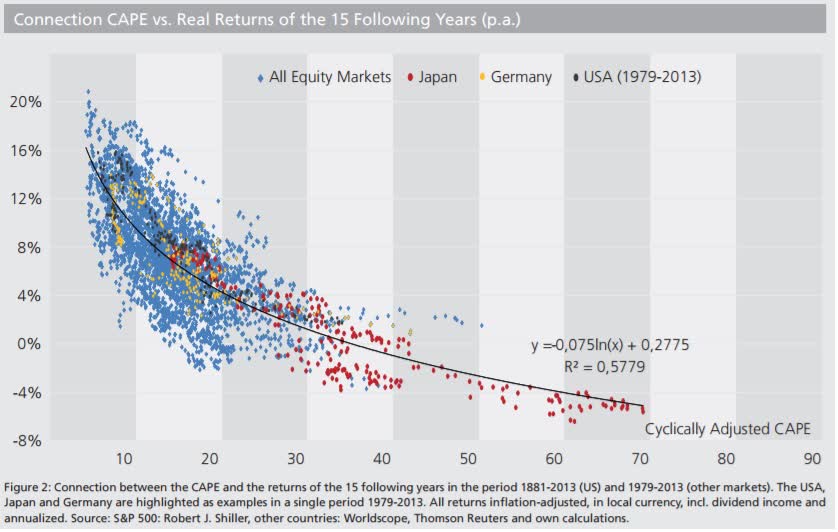
CAPE Ratio Vs. Real Returns (Lyn Alden)
All Aboard The Hype Train
If there’s one thing that’s worked over the past decade, it was holding U.S. tech stocks. Thus, the outperformance of QQQ, which has 50% of its holdings in information technology and another 30% or so in communication and consumer tech.

QQQ’s Sector Allocations (Invesco)
Invesco advertises this ETF by pointing out its track record of outperformance and its trading volume:

QQQ ETF (Invesco)
The problem is, tech stocks outperformed massively before the dot com bubble burst. Following the implosion of 2000, it took more than 15 years for the Nasdaq 100 to recover its losses:
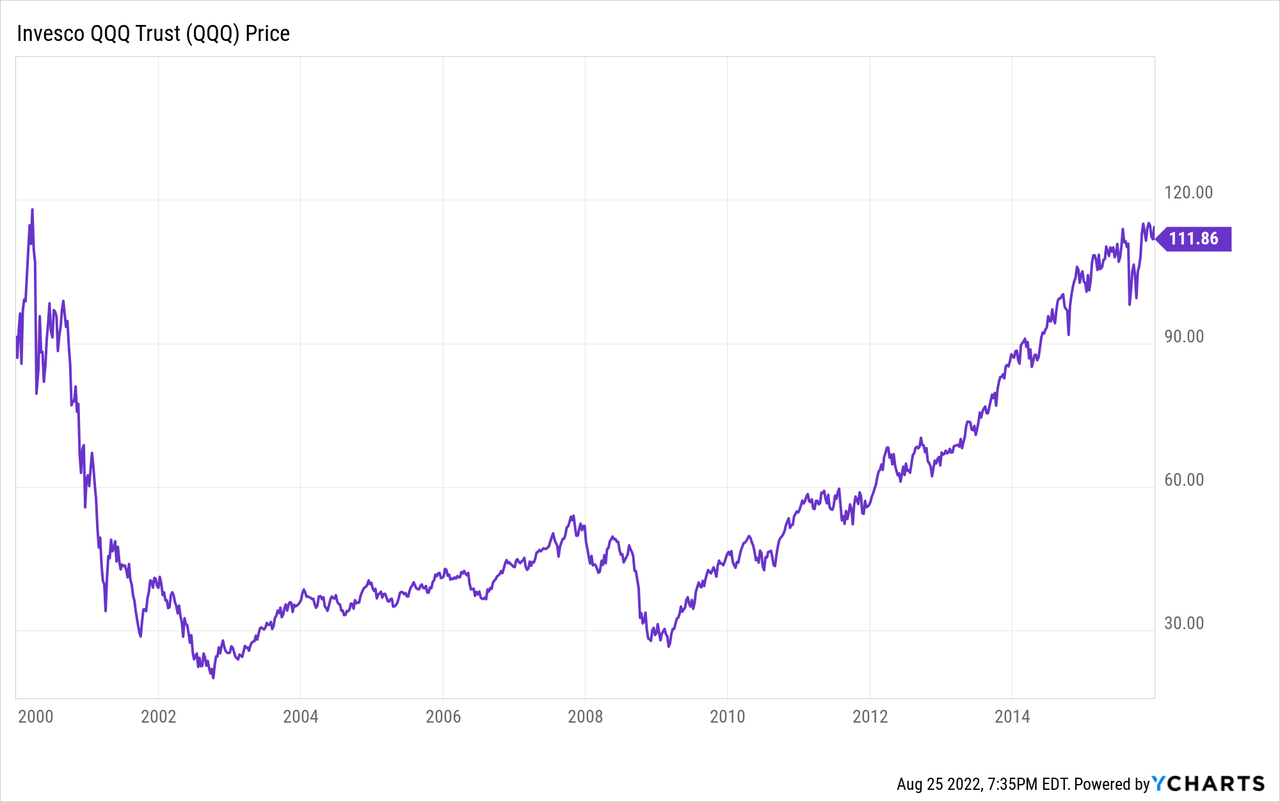
In fact, the reason QQQ has outperformed over the past 15 years is because tech underperformed from 2000 to 2010, in my opinion. This meant there were huge bargains in the sector as everyone was depressed about tech stocks. So you can see, you don’t want to buy what’s done well recently, in fact, you want to do just the opposite. We’ve studied several investors who outperformed the market over multiple decades, from Warren Buffett, to Carl Icahn, to Sir John Templeton, to Howard Marks. They all had one thing in common, they bought when there was blood in the streets. QQQ is concentrated in the hottest sectors of the past 5 years, and that’s not where you want to hunt for outsized returns:
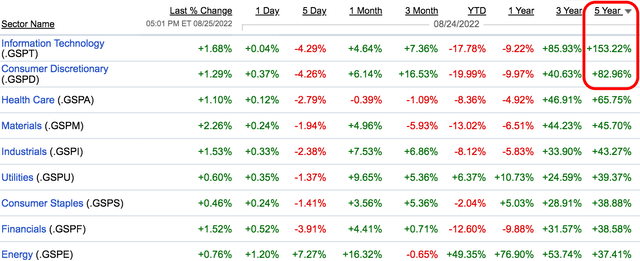
Sector Performance (Fidelity)
The average S&P 500 company survives only 20 years, and for tech stocks, that lifespan could be even shorter as these businesses face brutal competition, and the industry is constantly changing. If we look at businesses that survived for more than 200 years, we get banks like JPMorgan Chase (JPM), chemical companies like DuPont (DD), and consumer staples companies like Colgate-Palmolive (CL). These are simple and predictable businesses in industries that enjoy a very slow pace of change.
It’s About To Get Ugly
QQQ’s Top 10 Holdings

QQQ’s Top 10 Holdings (Invesco)
We’ve analyzed many of QQQ’s top holdings individually, including Apple (AAPL), Microsoft (MSFT), Amazon (AMZN), Tesla (TSLA), Google (GOOG) (GOOGL), Meta (META), and Costco (COST). Marked in red above are our expected annual returns for each business, with a 10-year time horizon. Overall, this equates to a 4% expected annual return for QQQ’s top holdings. In other words, you could get an inflation adjusted return of 0% per annum holding these stocks.
History has shown the market tends to swing from overly optimistic to overly pessimistic. Legendary investor George Soros coined this the boom-bust model. He believed that excessive margin, speculation, and exuberance on the upside creates excessive insolvency, fear, and selling on the downside. In other words, the larger the boom, the larger the bust. So, what do you think comes next for QQQ? If we had to wager, we’d bet on an excessive bust.
Risks To The Thesis
Crazy things can go on longer than you expect. In 1989, the PE of the Japanese index reached 60x earnings. The Nasdaq 100 is still nowhere near this level. Enthusiasm can always return in the short-run.
Also, while Sir John Templeton has cautioned against saying “this time is different,” he conceded that 20% of the time it really is different. Technology stocks have defied gravity up to this point. And, holding a diversified group of technology stocks with a 30-year time horizon isn’t a terrible idea. We’ve seen many of these businesses develop enduring moats and compound at a rapid pace for an extended period of time. An asset-light model and rapidly growing industry is generally a good place to be. Technology should be a part of everyone’s portfolio, at the right valuation.
Our Valuation
The Nasdaq 100 has a PE ratio of 27.2, but its earnings could still be at a cyclical peak, as evidenced by its much higher CAPE ratio. This means QQQ likely has earnings per share around $11.78. Looking at the aggregate of several QQQ businesses we’ve analyzed, combined with the cheaper, but slower growing businesses that round out the QQQ ETF, we believe EPS will grow at 8% per annum in the decade ahead. This growth should outpace the S&P 500’s EPS, but the valuation is more stretched than the S&P.
Our 2032 price target for QQQ is $445 per share, implying returns of 4% per annum with dividends reinvested.
- Growing QQQ’s EPS at 8% per annum, we get $25.43 per share in 2032. We’ve assigned a terminal multiple of 17.5x as we believe growth will slow slightly in the decade that follows. Keep in mind, this is a base-case scenario.
The Bottom Line
The risk and reward is unfavorable for QQQ, and some of the exuberance we saw on the upside could reverse on the downside. It’s possible you get inflation-adjusted returns of 0% per annum even after holding for 10 years. With such long-duration cash flows, QQQ is very susceptible to an increase in interest rates.
For more on this fund’s individual holdings, check out my analysis of Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, Tesla, Google, Meta, and Costco. Links are in the names.
What To Do About It
We’re projecting higher returns in communication companies like Meta and Google than other names in this ETF. Interestingly, communication services has been the worst performing sector of the past 5 years. There’s despondency here, and with despondency comes the potential for outsized returns. For ETF investors, we recommend Vanguard Communication Services ETF (VOX). Here are its top holdings:
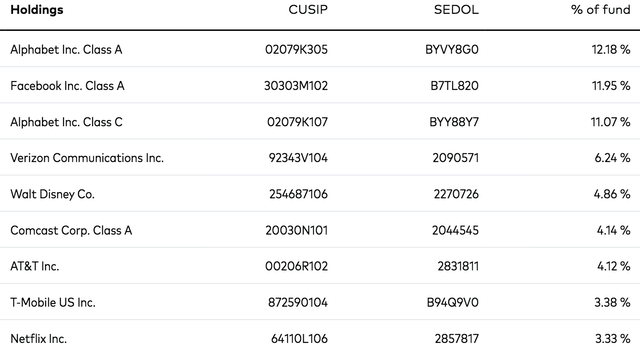
VOX Holdings (Vanguard)
Until next time, happy investing.
[ad_2]
Source links Google News

