[ad_1]
Opla/E+ via Getty Images
This monthly article series shows a dashboard with aggregate industry metrics in materials. It is also a top-down analysis of sector ETFs like the Materials Select Sector SPDR ETF (XLB) and the Fidelity MSCI Materials Index ETF (NYSEARCA:FMAT), whose largest holdings are used to calculate these metrics.
Shortcut
The next two paragraphs in italic describe the dashboard methodology. They are necessary for new readers to understand the metrics. If you are used to this series or if you are short of time, you can skip them and go to the charts.
Base Metrics
I calculate the median value of five fundamental ratios for each industry: Earnings Yield (“EY”), Sales Yield (“SY”), Free Cash Flow Yield (“FY”), Return on Equity (“ROE”), Gross Margin (“GM”). The reference universe includes large companies in the U.S. stock market. The five base metrics are calculated on trailing 12 months. For all of them, higher is better. EY, SY and FY are medians of the inverse of Price/Earnings, Price/Sales and Price/Free Cash Flow. They are better for statistical studies than price-to-something ratios, which are unusable or unavailable when the “something” is close to zero or negative (for example, companies with negative earnings). I also look at two momentum metrics for each group: the median monthly return (RetM) and the median annual return (RetY).
I prefer medians to averages because a median splits a set in a good half and a bad half. A capital-weighted average is skewed by extreme values and the largest companies. My metrics are designed for stock-picking rather than index investing.
Value and Quality Scores
I calculate historical baselines for all metrics. They are noted respectively EYh, SYh, FYh, ROEh, GMh, and they are calculated as the averages on a look-back period of 11 years. For example, the value of EYh for packaging in the table below is the 11-year average of the median Earnings Yield in packaging companies.
The Value Score (“VS”) is defined as the average difference in % between the three valuation ratios (EY, SY, FY) and their baselines (EYh, SYh, FYh). The same way, the Quality Score (“QS”) is the average difference between the two quality ratios (ROE, GM) and their baselines (ROEh, GMh).
The scores are in percentage points. VS may be interpreted as the percentage of undervaluation or overvaluation relative to the baseline (positive is good, negative is bad). This interpretation must be taken with caution: the baseline is an arbitrary reference, not a supposed fair value. The formula assumes that the three valuation metrics are of equal importance.
Current data
The next table shows the metrics and scores as of last week’s closing. Columns stand for all the data named and defined above.
|
VS |
QS |
EY |
SY |
FY |
ROE |
GM |
EYh |
SYh |
FYh |
ROEh |
GMh |
RetM |
RetY |
|
|
Chemicals |
-8.12 |
-5.65 |
0.0438 |
0.4049 |
0.0199 |
17.08 |
39.96 |
0.0439 |
0.4631 |
0.0225 |
17.95 |
42.70 |
-2.74% |
-9.00% |
|
Constr. Materials |
13.84 |
45.64 |
0.0503 |
0.8337 |
0.0207 |
17.95 |
29.51 |
0.0267 |
0.9092 |
0.0337 |
9.57 |
28.46 |
-7.20% |
-20.38% |
|
Packaging |
-30.22 |
7.78 |
0.0492 |
0.9170 |
0.0075 |
21.28 |
23.88 |
0.0477 |
1.0638 |
0.0375 |
17.59 |
25.25 |
-5.82% |
-11.91% |
|
Mining/Metals |
14.24 |
100 |
0.0822 |
1.2949 |
0.0049 |
23.30 |
25.99 |
0.0393 |
1.1594 |
0.0224 |
8.19 |
20.41 |
-16.53% |
-14.88% |
Value and Quality chart
The next chart plots the Value and Quality Scores by industry (higher is better).
Value and quality in materials (Chart: author; data: Portfolio123)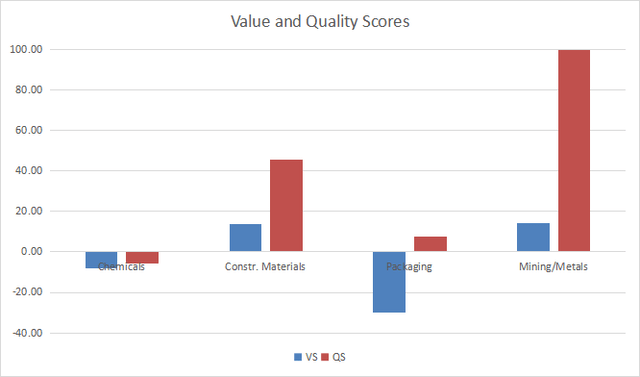
Evolution since last month
The most notable change is an improvement of both value and quality in mining/metals.
Variations in value and quality (Chart: author; data: Portfolio123)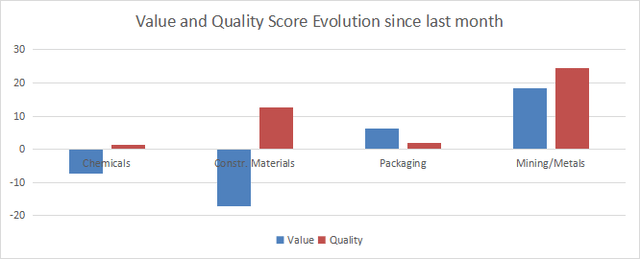
Momentum
The next chart plots momentum data.
Momentum in materials (Chart: author; data: Portfolio123)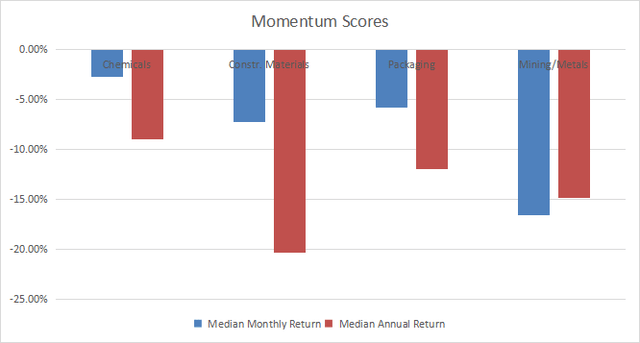
Interpretation
Construction materials and mining are undervalued by about 14% relative to 11-year averages. Moreover, they have excellent quality scores. The chemical industry is close below the historical baseline in both value and quality. Packaging is the less attractive industry here: it is overvalued by about 30% relative to the baseline. The quality is good, but not high enough to justify such overvaluation.
Focus on FMAT
The Fidelity MSCI Materials Index ETF (FMAT) has been tracking the MSCI US IMI Materials 25/50 Index since 10/21/2013. It has a total expense ratio of 0.08%: it is a bit cheaper than VAW, which tracks the same index for 0.10%, and XLB, which tracks a large cap only index for 0.12%.
The fund has 122 holdings. The next table lists the top 10 names with basic ratios and dividend yields. Their aggregate weight is about 48%.
|
Ticker |
Name |
Weight |
EPS growth %TTM |
P/E TTM |
P/E fwd |
Yield% |
|
LIN |
Linde plc |
12.62% |
41.27 |
38.66 |
25.26 |
1.56 |
|
SHW |
Sherwin-Williams Co |
5.41% |
-10.83 |
38.47 |
27.96 |
0.91 |
|
FCX |
Freeport-McMoRan Inc |
4.70% |
182.14 |
10.41 |
9.08 |
0.84 |
|
NEM |
Newmont Corporation |
4.59% |
-58.63 |
51.85 |
20.76 |
3.22 |
|
APD |
Air Products and Chemicals Inc. |
4.09% |
15.81 |
23.83 |
22.62 |
2.78 |
|
DOW |
Dow Inc |
3.88% |
249.44 |
7.28 |
8.40 |
4.19 |
|
NUE |
Nucor Corp |
3.49% |
418.40 |
4.51 |
4.86 |
1.59 |
|
ECL |
Ecolab Inc. |
3.45% |
185.27 |
41.79 |
30.77 |
1.27 |
|
CTVA |
Corteva Inc |
3.32% |
73.71 |
22.97 |
21.36 |
1.04 |
|
DD |
DuPont De Nemours Inc |
2.70% |
-47.67 |
21.19 |
18.59 |
2.08 |
FMAT and VAW share the same underlying index and have almost identical annualized returns since FMAT inception: 9.06% vs. 9.08%. Their maximum drawdown and volatility are also similar. As VAW is almost 10 years older, I will use it to assess FMAT index on a longer period.
VAW index has beaten XLB by a short margin of 41 bps in annualized return since inception. Their risk-adjusted performances are identical (Sharpe ratio in the table below).
|
since Feb. 2004 |
Annual. Return |
Drawdown |
Sharpe ratio |
|
FMAT index (VAW) |
9.33% |
-62.44% |
0.48 |
|
XLB |
8.92% |
-59.66% |
0.48 |
Data calculated with Portfolio123
In summary, FMAT is a good product for investors seeking capital-weighted exposure in basic materials. It currently holds 122 stocks including large, mid- and small caps, whereas XLB has only 29 holdings in large companies. Buy-and-hold investors may prefer FMAT for its cheaper management fees, whereas liquidity makes XLB a better instrument for tactical allocation and trading. Investors who are concerned by risks related to the top holding weight (over 12%) may prefer the Invesco S&P 500® Equal Weight Materials ETF (RTM).
Dashboard List
I use the first table to calculate value and quality scores. It may also be used in a stock-picking process to check how companies stand among their peers. For example, the EY column tells us that a chemical company with an Earnings Yield above 0.0438 (or price/earnings below 22.83) is in the better half of the industry regarding this metric. A Dashboard List is sent every month to Quantitative Risk & Value subscribers with the most profitable companies standing in the better half among their peers regarding the three valuation metrics at the same time. The list below was sent to subscribers several weeks ago based on data available at this time.
|
X |
United States Steel Corp |
|
LYB |
LyondellBasell Industries NV |
|
TSE |
Trinseo PLC |
|
CLF |
Cleveland-Cliffs Inc |
|
DOW |
Dow Inc |
|
FCX |
Freeport-McMoRan Inc |
|
CC |
Chemours Co |
|
UFPI |
UFP Industries Inc |
|
GEF |
Greif Inc. |
|
OI |
O-I Glass Inc |
It is a rotating list with a statistical bias toward excess returns on the long-term, not the result of an analysis of each stock.
[ad_2]
Source links Google News

