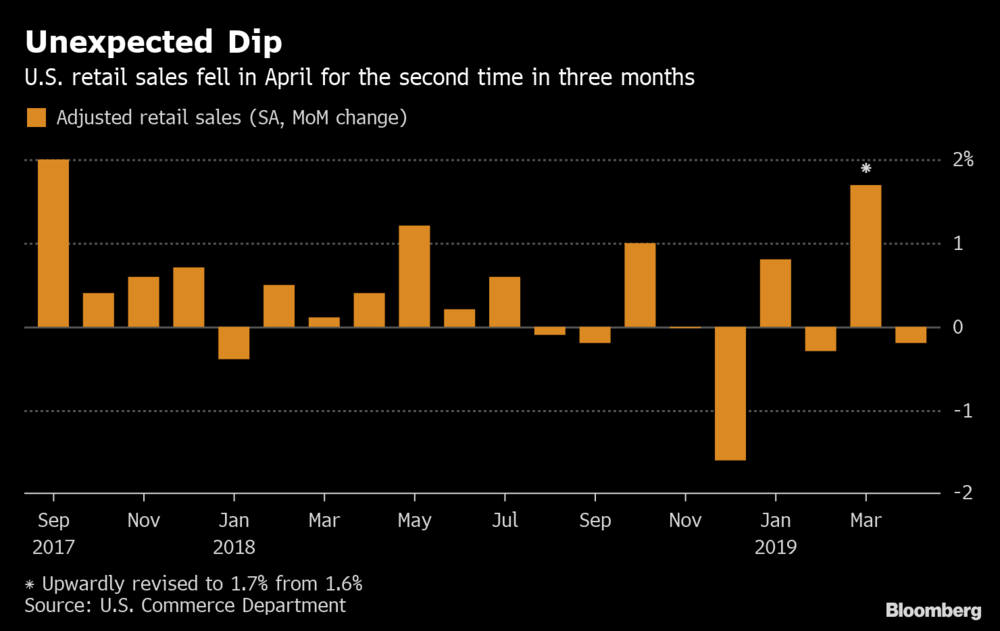
The value of overall sales declined 0.2% after a 1.7% increase the prior month that was the strongest gain since 2017, according to Commerce Department figures released Wednesday. That compared with the median forecast in Bloomberg’s survey calling for a 0.2% rise.
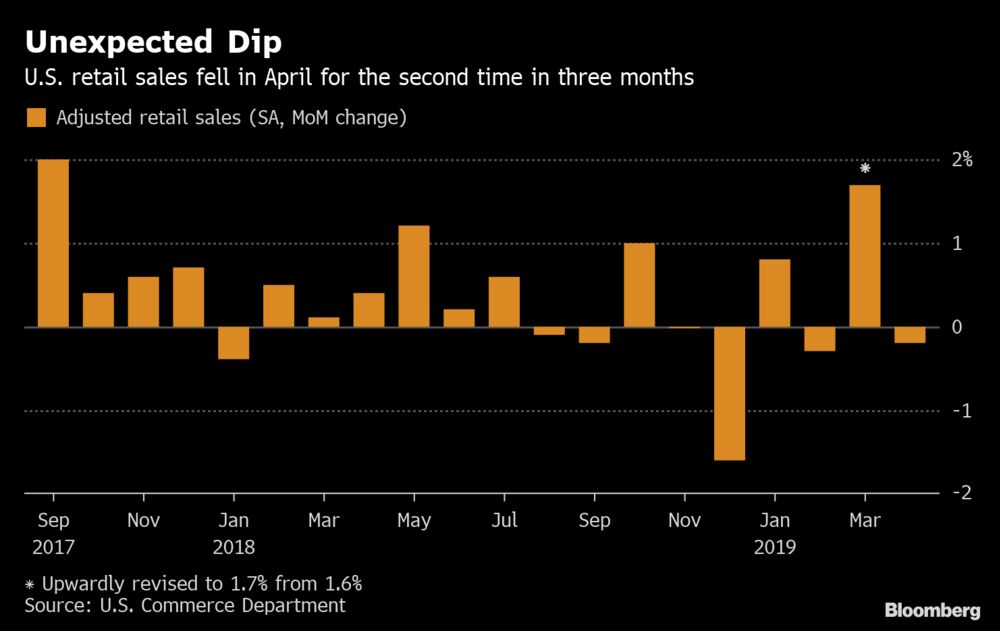
Sales in the “control group” subset, which some analysts view as a cleaner gauge of underlying consumer demand, were unchanged from the prior month, below projections for a 0.3% gain. The measure excludes food services, car dealers, building-materials stores and gasoline stations.
The figures, also reflecting weakness in the category that includes online sales, suggest spending remains soft following the weakest quarterly increase in a year. That could bolster pressure from President Donald Trump and financial markets to cut borrowing costs amid unexpectedly low inflation, though Federal Reserve policy makers have pledged patience as steady job and income gains should support purchases in coming months.
The retail report followed another round of downbeat data from the Fed showing U.S. factory production fell in April for a third time in four months with a broad decline led by weakness in machinery and motor vehicles. The cooler readings on the world’s largest economy followed reports from China that industrial output, retail sales and investment all slowed more than economists forecast in April, underscoring challenges to global growth from Trump’s widening trade war.
The U.S. retail data are “a bit of a downer for the near-term economic outlook but do not move the big picture needle much,” Stephen Stanley, chief economist at Amherst Pierpont Securities, said in a note. Recent seesaw patterns suggest there could be a “powerful bounceback in May.”
Retailers may be poised to take a further hit should Trump follow through on his threat to impose tariffs of 25% on almost all remaining Chinese imports, which would likely force Americans to absorb higher prices. Unlike the previous targets of U.S. levies, the majority of this tranche is consumer goods.
The report showed seven of 13 major retail categories decreased, with other down sectors including clothing, health and personal care, and electronics and appliances. Categories with increases included general merchandise, food and beverage stores, and restaurants and bars.
Sales at automobile dealers fell 1.1%, the most since January, after increasing 3.2% in the previous month. Industry data from Wards Automotive Group previously showed unit sales retreated in April, touching the lowest level since 2017.
Filling-station receipts increased 1.8%, the report showed, as oil prices rallied. The figures aren’t adjusted for price changes, so higher retail sales in the category could reflect higher gasoline costs, sales, or both.
Excluding automobiles and gasoline, retail sales fell 0.2% following a 1.1% increase.
The SPDR S&P Retail ETF (XRT) was trading at $42.90 per share on Wednesday morning, down $0.15 (-0.35%). Year-to-date, XRT has declined -4.78%, versus a 7.20% rise in the benchmark S&P 500 index during the same period.
XRT currently has an ETF Daily News SMART Grade of A (Strong Buy), and is ranked #4 of 41 ETFs in the Consumer-Focused ETFs category.
This article is brought to you courtesy of Bloomberg.